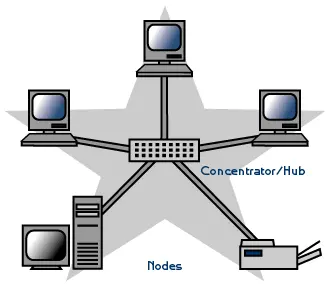
Star topology is a common network configuration in which all nodes or devices are connected to a central device or hub, forming a star-shaped structure. This setup enables efficient communication, easy expansion, and robust performance.
In this topology, every node (such as file servers, workstations, and peripherals) is directly connected to a central hub, switch, or concentrator, which acts as the central connection point for the entire network.
On a star network, all data communications flow through the central device (hub, switch, or concentrator) before being forwarded to their final destination.
All network functions are managed and controlled by the hub, switch, or concentrator. It functions as a repeater of data flow as well.
ref:googleimage
Table of Contents
Key Features
1. Centralized Connection: All devices connect to a central hub or switch.
2. Point-to-Point Connections: Each device has a dedicated connection to the central hub.
3. No Interdevice Communication: Devices communicate only through the central hub.
Advantages of Star Topology:
1. Easy Installation: Star topology is simple to set up and install.
2. Scalability: With ease of device addition, it’s perfectly suited for networks scaling up or expanding their infrastructure.
3. Fault Tolerance: If one device fails, others remain unaffected.
4. Centralized Management: The central hub enables easy monitoring and control.
5. Improved Performance: This topology can handle high-traffic networks with ease.
6. Reduced Collisions: Since providing each device with its dedicated connection, collisions are decreased, allowing for more efficient network performance.
7. Easy Troubleshooting: Issues can be isolated to individual devices or the central hub.
8. Flexibility: This topology can be used with various network protocols and devices.
9. Security: The central hub can be used to implement network security measures.
10. Cost-Effective: While the initial cost may be higher, star topology can be more cost-effective in the long run.
11. Easy Maintenance: This topology allows for simple maintenance and repair of individual devices, without disrupting the operation of the entire network.
12. Improved Security: This topology allows centralized security management and monitoring.
13. Reduced Interference: This topology reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio-frequency interference (RFI).
14. Flexible Connectivity: This topology supports various connections, including copper, fiber, and wireless.
15. Scalable Bandwidth: This topology allows easy upgradation to increase bandwidth and network capacity.
Disadvantages of Star Topology:
1. Single Point of Failure: A failure of the central hub can lead to a complete network shutdown.
2. Dependence on Central Hub: All communication relies on the central hub.
3. Higher Cost: Requires a central hub, increasing overall cost.
4. Limited Distance: The distance between devices and the central hub can be limited.
5. Bottleneck: If the central hub is underpowered, it can become a chokepoint, restricting network throughput.
6. Difficult Rearrangement: Rearranging devices can be difficult due to the fixed connections.
7. Cable Damage: Damage to cables can affect multiple devices.
8. Limited Expandability: While scalable, star topology can become complex with too many devices.
9. Power Dependence: The central hub requires power, which can be a concern in power outages.
10. Upgrade Challenges: Upgrading the central hub can be challenging and costly.
11. Dependence on Central Hub: The entire network relies on the central hub, which can be a single point of failure.
12. Limited Redundancy: Star topology does not provide built-in redundancy, which can lead to network downtime.
13. Difficult Cable Management: Star topology can result in complex cable management and organization.
14. Limited Flexibility: Star topology can be inflexible when it goes down to changing network configurations.
15. Vulnerability to Physical Damage: This topology is vulnerable to physical damage to the central hub or cables.
Applications of Star Topology:
1. Local Area Networks (LANs): Star topology is commonly used in LANs for its ease of use and scalability.
2. Wireless Networks: Star topology is used in wireless networks, with the central hub acting as a wireless access point.
3. Data Centers: Star topology is used in data centers for its centralized management and scalability.
4. Campus Networks: This topology is used in campus networks to connect buildings and departments.
5. Industrial Control Systems: This topology is used in industrial control systems to connect sensors, actuators, and controllers.
6. Medical Facilities: Thistar topology is a common network configuration in which all nodes or devices are connected to a central device or hub, forming a star-shaped structure topology is used in the medical field to connect medical devices, patient rooms, and nurse stations.
7. Financial Institutions: This topology is used in financial institutions to connect branches, ATMs, and data centers.
8. Transportation Systems: This topology is used in transportation systems to connect traffic management centers, sensors, and cameras.
9. Smart Homes: This topology is used in smart homes to connect devices, sensors, and controllers.
10. Aerospace and Defense: Star topology is used in aerospace and defense applications to connect communication systems, radar, and sensors.
11. Data Centers: Star topology is used in data centers to connect servers, storage, and network devices.
12. Virtual Reality: This topology is used in virtual reality applications to connect VR devices, sensors, and controllers.
13. Internet of Things (IoT): This topology is used in IoT applications to connect devices, sensors, and gateways.
14. Wireless Networks: This topology is used in wireless networks to connect access points, clients, and gateways.
15. Cable Television: This topology is used in cable television networks to connect headends, nodes, and subscribers.
16. Telecommunications: Star topology is used in telecommunications networks to connect switches, routers, and gateways.
17. Gaming Networks: This topology is used in gaming networks to connect servers, clients, and gaming devices.
18. Scientific Research: This topology is used in scientific research applications to connect instruments, sensors, and data acquisition systems.
FAQs of Related topic
1. What is a star topology?
A star topology is a network configuration where all devices are connected to a central node, like a hub or switch. This central node acts as a communication hub, relaying data between connected devices.
2. What are the advantages of a star topology?
- Easy to install and expand: Adding or removing devices is simple without disrupting the entire network.
- Centralized management: The central node simplifies network monitoring and troubleshooting.
- Improved performance: Each device has a dedicated connection to the central node, reducing collisions and improving data transmission speed.
- Fault isolation: If one device or cable fails, it doesn’t affect the rest of the network.
3. What are the disadvantages of a star topology?
- Single point of failure: A failure at the central node results in a complete network outage.
- Cost: Requires more cabling compared to other topologies, potentially increasing costs.
- Dependent on the central node: The network’s performance is significantly influenced by the central node’s capacity and capabilities.
4. Where is star topology commonly used?
- Local Area Networks (LANs): Star topology is the most common configuration for LANs in homes, businesses, and schools due to its ease of management and scalability.
- Wireless networks: Wireless access points often act as the central node in a star topology, connecting multiple devices wirelessly.
5. How does star topology compare to other network topologies?
- The enhanced performance and fault isolation capabilities of star topology, when contrasted with bus topology, are accompanied by a higher cost.
- While star topology offers easier expansion and management than ring topology, it’s vulnerable to a single point of failure.
- Mesh topology provides greater redundancy than star topology but is significantly more complex and costly.
