- Modulation is defined as a process of converting a low-frequency signal into a high-frequency signal.
- OR
- Modulation is defined as the process of frequency translation. The spectrum of the signal shifted from a low-frequency region to a high-frequency region.
- OR
- Modulation is the process of converting a low-pass signal into a bandpass signal.
- The objective of demodulation is to convert the high-frequency signal back into the low-frequency signal.
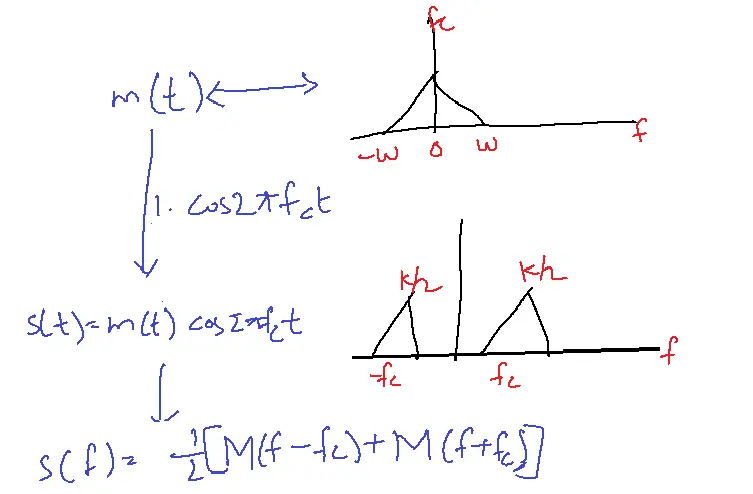
If a signal is multiplied with a carrier the spectrum will be shifted to the left side and right side by fc and the amplitude becomes half.
Table of Contents
Definition of Modulation in the Time domain:
Modulation is defined as the process in which a parameter of the carrier is varied according to the message signal. Assume that the message is exponentially decaying and the channel is free space.
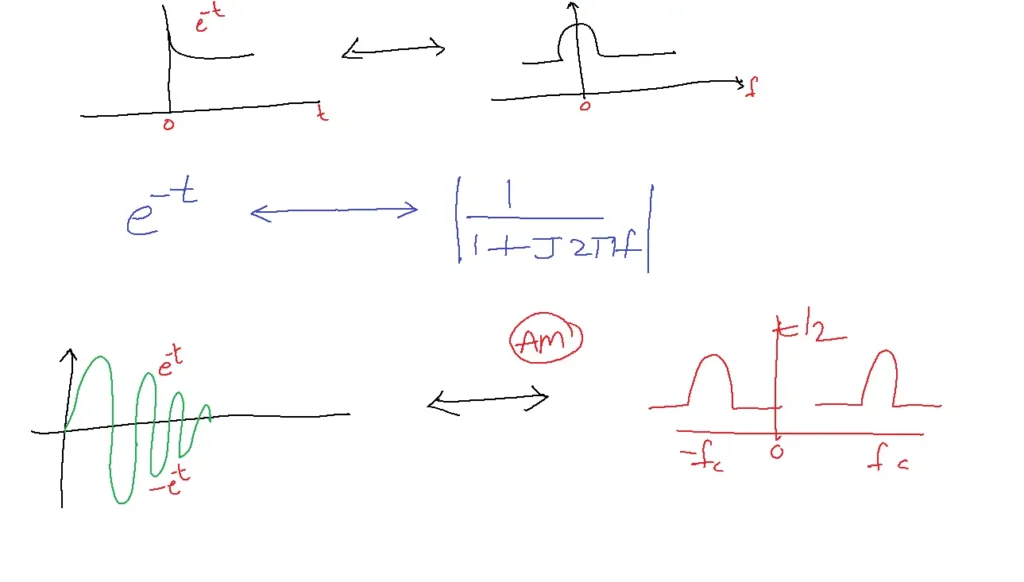
In this example, the amplitude of the carrier is varied according to the message signal. Before modulation the amplitude is constant. After modulation amplitude is the same as the message signal. So the above example represents the amplitude modulation.
The generalized equation of the carrier is:
C(t) = Accos[2πfct+pi]
In this equation Ac represents Amplitude Modulation, fc represents Frequency Modulation, and pi represents Phase Modulation.
The three parameters of the carrier which can be varied according to the message are amplitude, frequency, and phase.
The three basic Analog techniques are:
1. Amplitude Modulation
2. Frequency Modulation
3. Phase Modulation.
What is Need for Modulation?
1. Need for Modulation is to reduce the size of the antenna – Practically the size of the antenna depends on the wavelength. Voice, Audio, and Video signals have significantly low frequencies, so the size of the antenna required is very high. The transmission of signals into free space is not possible. To overcome this problem modulator is used which will convert a low-frequency signal into a high-frequency signal. As frequency increases the size of the wavelength decreases and the size of the antenna also increases.
2. Need for Modulation is for Multiplexing of Signals- Transmission of more than one signal through the same communication channel is called multiplexing. But multiplexing is possible with modulation only. In AC FDM is used.
3. Modulation is needed to reduce the effect of noise. If a signal is transmitted through a noise or channel distortion occurs due to noise, To determine this effect, the S/N ratio is used. However, the S/N ratio depends upon the type of modulation techniques.
4. Need for Modulation is for frequency allocation- In communication systems interference occurs if the frequencies are the same. To overcome this problem modulation is used. It is possible to allocate different frequencies so that interference will not occur.
5. Need for Modulation to overcome equipment limitations- Most communication equipment will work satisfactorily in a certain frequency range only. To overcome this problem modulation is used.
General block diagram of communication system
The main objective of a communication system is to transfer information from one place to another place using electrical signals.
The following signals are considered in analyzing communications.
1. Voice-300-3.5KHz-Telephone
2. Audio-20-20KHz-Radio
3. Video-0-4.5MHz-TV
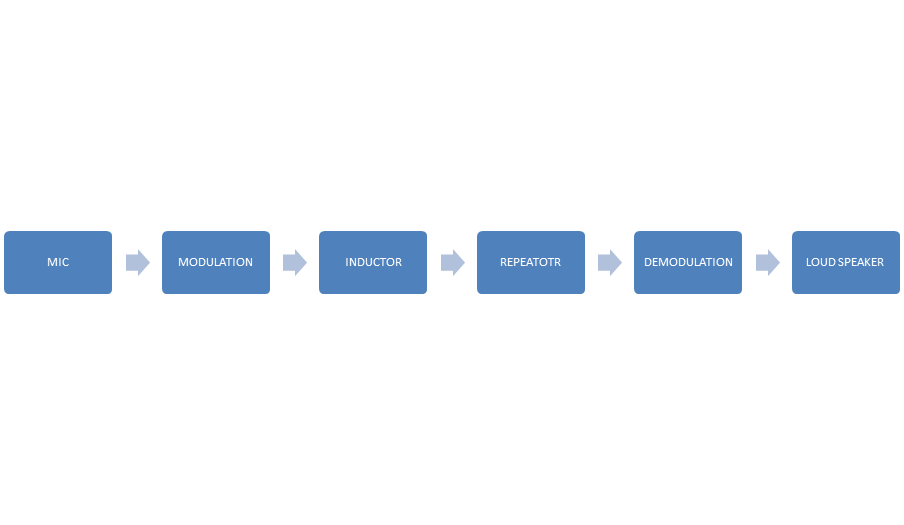
- Here inductor means FOC or twister pair or coaxial cable or free space.
- In the block diagram, Voice is given to MIC as input and the process continues till the loudspeaker also gives voice as output.
- A microphone or Transducer is required to convert a non-electrical signal into an electrical signal.
- The modulator is used to modify the electrical signal according to the requirements. The output of the modulator is transmitted from one place to another using a communication channel.
- Due to various losses the signal strength gradually decreases. So repeaters are used to increase the signal strength. Then the number of repeaters depends on the distance and type of cable used.
- The demodulator is used to re-modify the signal and the transducer is required to convert the electrical signal into its original form.
Fourier Transform:
Fourier transform concept is required to determine the frequencies present in a signal.
Fourier transform converts a time domain signal into a frequency domain signal.
The graphical representation of the frequency domain signal is called a spectrum. It is possible to determine the frequencies from the spectrum.
Consider a signal m(t) and m(f)
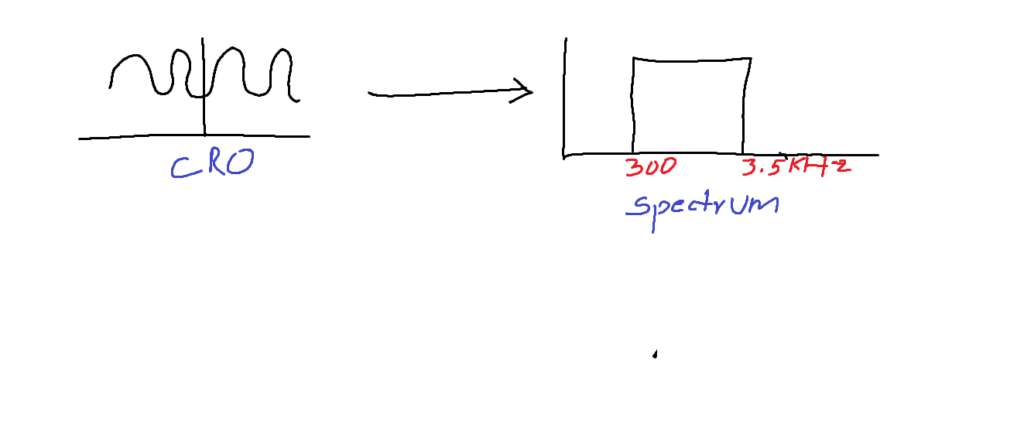
Practically CRO is used to time domain signal and a spectrum analyzer is used to observe the frequency domain signal.
Signal Bandwidth is defined as the range of frequencies occupied by the signal.
Bandwidth = fH – fL
= 10 KHz.
Practically signal bandwidth should be minimum and channel Bandwidth should be maximum.
The following 4 parameters are considered in designing a communication system:
1. Bandwidth
2. Power
3. Signal to Noise Ratio
4. Receiver Complexity
m(t) = message signal
m(t) = modulating signal
m(t) = Base band signal
Any signal having low frequencies is called the baseband signal.
By doing the Fourier transform, m(t) is converted to M(f).
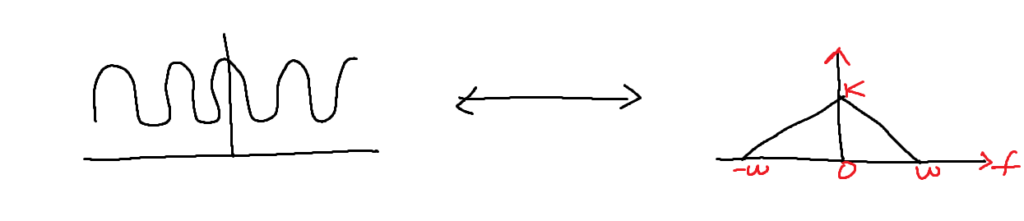
w=highest frequency of M(f)
c(t)= carrier signal
Carrier is always a very high-frequency sinusoidal signal.
A carrier is used to convert a low-frequency signal into a high-frequency signal.
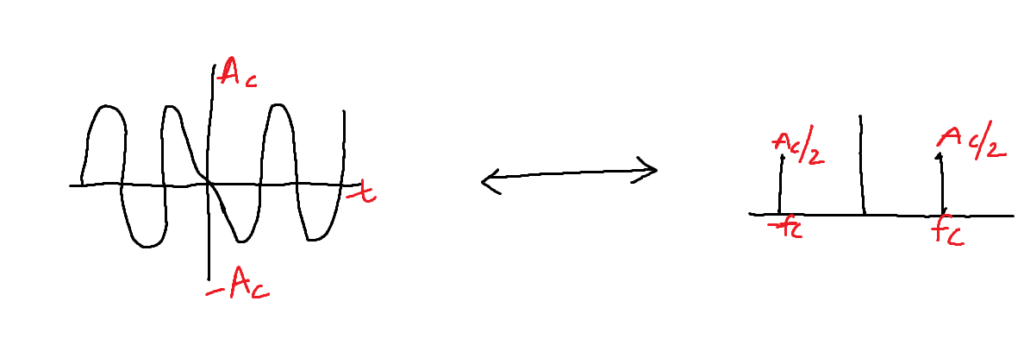
S(t)=Modulated Signal
=M(t).C(t)
