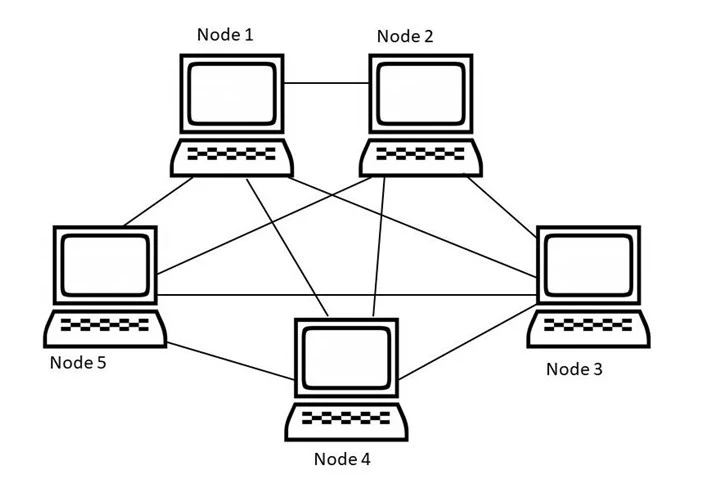
- Mesh topology is a network configuration where each device is connected to every other device, forming a web-like structure. This configuration offers multiple data pathways, ensuring that data can still be transmitted even if one route is disrupted, thereby providing redundancy and fault tolerance.
- This novel network architecture establishes point-to-point connections between the network’s devices by connecting every computer to every alternate computer. In a mesh network, messages can take multiple routes to reach their destination, offering flexible and adaptive pathways that differ from the more structured approaches of previous topologies.
- A full mesh network is one in which every device is connected to every other device. One drawback of mesh networks with n nodes is that each node needs n-1 I/O ports, or links, and a mesh network with n nodes needs n(n-1)/2 links.
ref: google image
Table of Contents
Key Features of Mesh Topology
1. Multiple Connections: Each device has multiple connections to other devices.
2. Redundancy: Multiple paths for data to travel between devices.
3. Fault Tolerance: When a connection goes down, data can instantly reroute through alternative connections, maintaining uninterrupted data transfer.
4. Scalability: This topology can support a large number of devices.
Advantages of Mesh Topology:
1. High Reliability: This topology provides high reliability due to redundancy.
2. Fault Tolerance: This topology can withstand device failures.
3. Scalability: This topology can support a large number of devices.
4. Flexible: This topology allows for flexible network configuration.
5. Improved Performance: This topology can improve network performance.
6. Improved Network Reliability: This topology’s multi-path approach ensures that data can always find a way to reach its destination, greatly reducing the risk of network failure and promoting high uptime.
7. Enhanced Fault Tolerance: In the case of a device or connection failure, data can seamlessly bypass the affected area and continue its journey through alternative connections.
8. Increased Scalability: This topology can support more devices and connections.
9. Flexible Network Configuration: This topology allows for flexible network configuration and adaptation.
10. Better Network Performance: This topology can improve network performance by reducing latency and increasing bandwidth.
11. Improved Security: This topology can provide better security by allowing redundant connections and encryption.
12. Easy Maintenance: This topology simplifies maintenance and repair tasks, allowing devices and connections to be easily accessed, updated, and restored with minimal disruption.
13. Reduced Network Congestion: Mesh topology can reduce network congestion by providing multiple paths for data to travel.
14. Improved Quality of Service (QoS): This topology can provide bettered QoS by prioritizing traffic and ensuring reliable connections.
15. Support for Real-Time Applications: This topology can support real-time applications by providing low latency and high availability.
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology:
1. Complexity: This topology can be complex to set up and manage.
2. High Cost: This topology requires more hardware and cabling.
3. Difficult Troubleshooting: Issues can be hard to identify and isolate.
4. Limited Security: This topology can be vulnerable to security threats.
5. High Power Consumption: This topology can consume more power due to the multiple devices and connections.
6. Difficult Upgrade and Expansion: This topology can be difficult to upgrade and expand due to the complex network structure.
7. Dependence on Network Management: This topology requires effective network management to ensure reliable connections.
8. Vulnerability to Physical Damage: This topology is vulnerable to physical damage to devices and connections.
9. Limited Compatibility: This topology may have less compatibility with certain devices or networks, requiring specific hardware or software configurations to function seamlessly.
10. Steep Learning Curve: This topology requires specialized knowledge and skills to set up and manage.
Applications of Mesh Topology:
1. Wide Area Networks (WANs): This topology is used in WANs for reliability.
2. Wireless Networks: This topology is used in wireless networks for coverage.
3. Sensor Networks: This topology is used in sensor networks for data collection.
4. Peer-to-Peer Networks: This topology is used in peer-to-peer networks for file sharing.
5. Cloud Computing: This topology is used in cloud computing for data centers.
6. Industrial Automation: This topology is used within industrial automation systems to connect devices and enable real-time communication.
7. Smart Grids: This topology is used in smart grids to connect devices and enable real-time communication.
8. Medical Device Networks:This topology is used in medical device networks to connect devices and enable real-time communication.
9. Aerospace and Defense Networks: Mesh topology is used in aerospace and defense networks to connect devices and enable secure communication.
10. Underwater Sensor Networks: Mesh topology is used in underwater sensor networks to connect sensors and collect data.
11. Environmental Monitoring Networks: Mesh topology is used in environmental monitoring networks to connect sensors and collect data.
12. Smart Home Networks: Mesh topology is used in smart home networks to connect devices and enable automation.
13. Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Mesh topology is used in logistics and supply chain management to connect devices and enable real-time tracking.
14. Public Safety Networks: Mesh topology is used in public safety networks to connect devices and enable secure communication.
15. Disaster Recovery Networks: Mesh topology is used in disaster recovery networks to connect devices and enable communication in an emergency.
FAQs of Mesh Topology
1. What is a mesh topology?
- A mesh topology is a network configuration where each device (node) is connected to multiple other nodes, creating a web-like structure.
- Data can travel through various paths, enhancing redundancy and reliability.
2. What are the advantages of a mesh topology?
- High fault tolerance: If one connection fails, data can be rerouted through other paths, minimizing downtime.
- Improved reliability: Multiple connections ensure continuous communication even if some nodes fail.
- Increased bandwidth: Data can be transmitted simultaneously across multiple links, potentially increasing overall bandwidth.
- Scalability: Adding new nodes is relatively easy without disrupting the existing network.
3. What are the disadvantages of a mesh topology?
- High complexity: Configuring and managing a mesh network can be complex due to the numerous interconnections.
- High cost: The extensive cabling and hardware required for numerous connections can be expensive.
- Redundancy overhead: Maintaining multiple paths for data transmission can lead to increased network overhead.
4. Where is mesh topology commonly used?
- Wireless networks: Mesh topology is frequently used in wireless mesh networks (WMNs) for large-scale coverage and self-healing capabilities.
- Critical infrastructure: This technology finds applications in scenarios demanding exceptional reliability, including military networks, industrial automation systems, and the infrastructure supporting smart cities.
5. What are the different types of mesh topology?
- Full mesh: Each node has a direct connection to every other node, resulting in unparalleled redundancy at the cost of increased complexity.
- Partial mesh: Only some nodes are directly connected to others, balancing cost and redundancy.
