What is a Linked List?
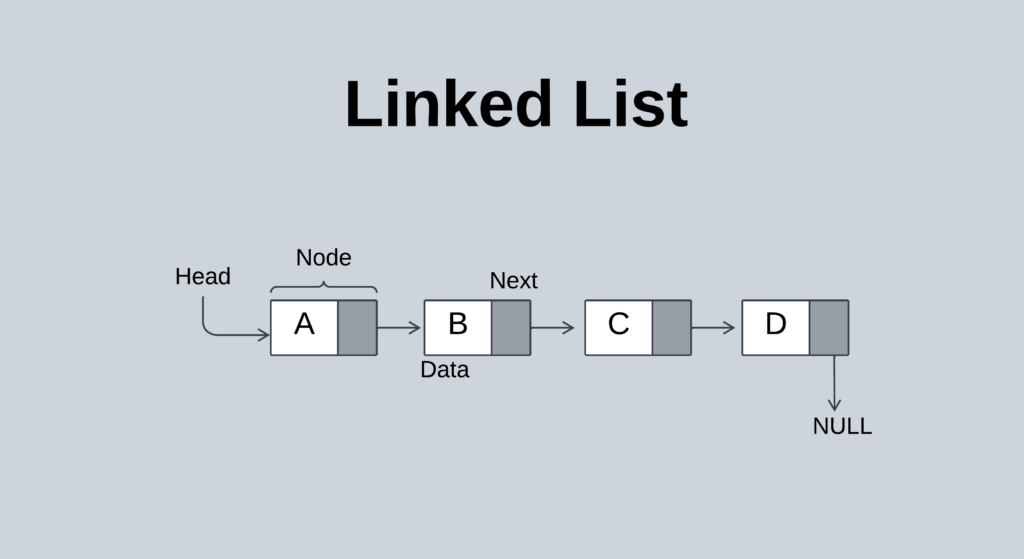
- In computer science, a linked list is a linear collection of data elements called nodes.
- Each node of the linked list consists of data and links. Data can hold various types of information, including integers, characters, and more.
- The link of the node contains the address of the next node.
- The link is a pointer which points to the next node.
- The last node of the linked list will have no connection with the other node. So fill the link field of the final node with a NULL value.
- In C language the node can be represented using self-referential structure. Linked lists are simple and most commonly used data structure.
- They can be used to implement other data structures such as stacks, queues, etc…
Ex:
| data | link |
Node
Types of Linked Lists:
Table of Contents
Difference between Array and Linked List
| Array | Linked List |
| An array is a collection of similar data items stored under a common name. | A linked list is a sequential collection of elements connected by pointers. |
| In an array, elements can be accessed randomly. | Linked lists require sequential access to their elements. |
| In an array, elements are stored in consecutive memory locations. | Linked lists offer flexibility in memory allocation, as elements can be placed in any available space, with the address of the following value stored in the current node. |
| Inserting or deleting elements in arrays can be slower compared to other data structures due to the consecutive storage of elements | Linked lists offer efficient insertion and deletion operations because we only need to modify pointers. |
| In arrays, memory is allocated at compiler time. | In linked lists, memory is allocated at run time. |
| Arrays can be 1-D, 2-D, multi-dimensional arrays. | Linked lists may be singly linked lists, doubly-linked lists, and circular linked lists. |
| In arrays each element is independent. | In the linked list each element is dependent. |
| Unlike linked lists, arrays don’t require pointers, eliminating the need for extra memory to store them. | In the linked list adjacency between the elements is maintained with the help of pointers. So we require extra space to store the pointer. |
Applications of Linked List:
The two most important applications of linked lists are polynomial representation and sparse matrix.
Polynomials consist of various terms, each containing a coefficient and an exponent. A polynomial P(x) is in the form of
P(x) = Axn+Bxn-1++Cxn-2+….+yx+z
Where A, B, C,……., Z are real numbers and n is a non-negative integer called the degree of the polynomial.
Ex: 6x3+9x2+7x+4
Each term in a polynomial is represented as a node.
A node consists of a coefficient, an exponent, and a link.
Advantages of Linked List:
- Dynamic Sizing: Linked lists adjust their size dynamically, eliminating the risk of overflow errors common to fixed arrays.
- Efficient Insertions/Deletions: Adding or removing elements in linked lists is efficient, especially at the beginning or middle, as it doesn’t require shifting elements like arrays.
- Memory Efficiency: Linked lists allocate memory only as needed, optimizing memory usage compared to arrays, which might allocate more space than required.
- Building Block for Advanced Structures: Linked lists are foundational for building more complex data structures like stacks, queues, trees, and graphs, extending their utility.
- Representing Data Relationships: Linked lists effectively model relationships between data elements in simple sequences or complex networks, providing a clear representation.
Disadvantages of Linked List:
- Random Access is a No-G
- Memory Overhead: The Price of Flexibility
- Cache Unfriendly: Slowing Down Performance
- Reverse Traversal Challenges (Singly Linked Lists)
- Complexity in Implementation
