Pulse Amplitude Modulation is one of the techniques used in Pulse Modulation.
Pulse Modulation Techniques:
In pulse analog modulation samples are applied as input to the modulator. High-frequency periodic rectangular pulses are used as the carrier. The three parameters of the carrier can be varied according to the sampled value or pulse amplitude, pulse width, and pulse position.
The three pulse modulation techniques are:
1. Pulse Amplitude Modulation
2. Pulse Width Modulation
3. Pulse Position Modulation
Table of Contents
In this Pulse Amplitude Modulation method, the amplitude of the periodic rectangular pulses is varied according to the sampled value.
The amplitude of an analog signal sample is used to adjust the amplitude of a constant width, constant width, and constant position. While PWM and PPM have distinct waveforms, this method produces a waveform that more faithfully represents the original analog signal. Ethernet and phone modems use Pulse Amplitude Modulation faster than 300 bits per second.
Pulse Amplitude Modulation is divided into two types:
i. Single Polarity PAM
ii. Double Polarity PAM
Single Polarity PAM:
Single-polarity PAM generates a modulated signal with a single polarity, meaning the signal’s amplitude variations are either exclusively above or below the zero baseline.
Note: The bandwidth of a rectangular pulse depends on the pulse width. This implies that as pulse width decreases, bandwidth increases, and vice versa.
Generation of Single Polarity PAM:
This method involves adding a DC bias to the message signal, ensuring the resulting signal remains positive. This signal is applied to a multiplier along with periodic rectangular pulses. The output represents the single polarity PAM.
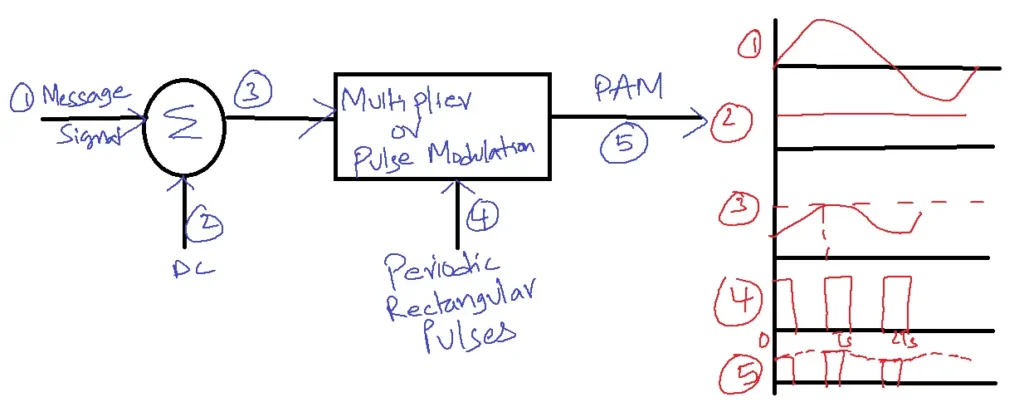
In this single-polarity PAM method, the pulse amplitude is varied according to the sampled value. If the sampled value is maximum, the pulse amplitude will also be maximum.
The bandwidth of the PAM signal is constant. The power needed for signal transmission varies. As the amplitude of the PAM signal changes, power also changes.
The spectrum of the PAM signal:
Demodulation of PAM:
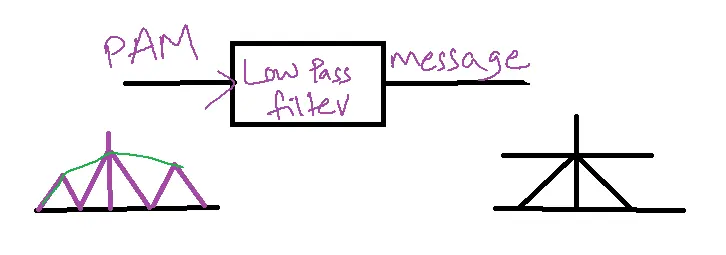
LPF is used as the demodulator for the PAM signal.
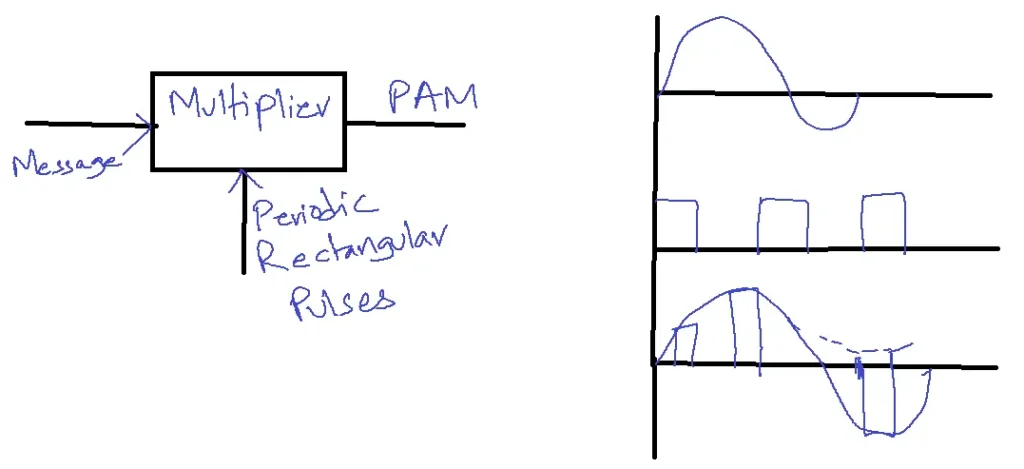
Double Polarity PAM:
In this method, the output of the modulator will have both polarities. The message signal is applied to the multiplier without adding any DC component.
Applications of Pulse Amplitude Modulation:
- Digital Communication Systems: PAM is the foundation for various digital modulation schemes, including Pulse Code Modulation (PCM). This makes it crucial for transmitting voice, data, and video signals over digital networks.
- Ethernet Communication: PAM is crucial in Ethernet local area networks (LANs). It enables the efficient transmission of data packets over twisted-pair cables, contributing to the widespread use of Ethernet in homes and businesses.
- Optical Fiber Communication: Optical fiber communication systems extensively utilize PAM as a modulation technique. It modulates the intensity of light pulses to transmit information over long distances at high speeds, making it essential for internet infrastructure and telecommunications.
- Instrumentation and Control Systems: PAM is used in various measurement and control applications. It converts analog sensor signals into digital form for processing and analysis, enabling precise monitoring and control of industrial processes.
- Radar and Navigation Systems: PAM is employed in radar systems for pulse modulation, allowing for the detection and tracking of objects. Beyond its other applications, it plays a key role in navigation systems by providing precise distance and position information.
Related FAQ’s
1. What is Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM)?
- PAM is a modulation technique where the amplitude of a pulse carrier signal is varied in proportion to the instantaneous amplitude of the message signal.
- It’s a fundamental building block for various digital modulation schemes.
2. What are the different types of Pulse Amplitude Modulation?
- The main types of PAM are:
- Single Polarity PAM: All pulses have positive amplitude.
- Double Polarity PAM: Pulses can have both positive and negative amplitude.
- Natural PAM: Pulse amplitude follows the natural shape of the message signal.
- Flat Top PAM: Pulse amplitude is held constant for the duration of the pulse.
3. What are the applications of PAM in ECE?
- PAM finds widespread use in:
- Digital communication systems: As a basis for PCM and other digital modulation schemes.
- Ethernet communication: For data transmission over twisted-pair cables.
- Optical fiber communication: For modulating light intensity in long-distance transmission.
- Instrumentation and control systems: For converting analog sensor signals to digital form.
- Radar and navigation systems: For pulse modulation and distance measurement.
4. What are the advantages and disadvantages of PAM?
- Advantages:
- Simple implementation.
- Compatible with both analog and digital signals.
- Serves as a foundation for more complex modulation schemes.
- Disadvantages:
- Susceptible to noise and interference.
- Requires a larger bandwidth compared to other modulation techniques.
- It balances performance and power efficiency, though other digital modulation schemes may demonstrate higher efficiency.
5. How is PAM different from other pulse modulation techniques?
- PAM varies pulse amplitude, while other techniques like:
- Pulse Width Modulation (PWM): Varies pulse width (duration).
- Pulse Position Modulation (PPM): Varies pulse position (timing).
