What is Phase Shift Keying?
Phase Shift Keying (PSK) is a digital modulation technique used to transmit data by modifying the phase of a carrier wave. This method is widely used in communication systems, including wireless networks, satellite communication, and fiber optic transmission.
How Does PSK Work?
1. Carrier Wave Generation: A high-frequency carrier wave is generated.
2. Data Encoding: Digital data (0s and 1s) is encoded onto the carrier wave by shifting its phase.
3. Phase Shift: The phase of the carrier wave is shifted according to the data being sent.
4. Transmission: The modulated carrier wave is transmitted through the channel.
5. Demodulation: The received signal is demodulated to extract the original data.
Types of PSK
1. Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK): 2-phase shifts (0° and 180°) for binary data.
2. Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK): 4-phase shifts (0°, 90°, 180°, and 270°) for 2-bit data.
3. 8-Phase Shift Keying (8PSK): 8-phase shifts for 3-bit data.
4. Differential Phase Shift Keying (DPSK): Phase shifts are relative to the previous symbol.
In phase shift keying, the phase of the carrier signal changes concerning binary data.
Table of Contents
Binary phase shift keying(BPSK):
There are two phases:
1. Zero-degree phase
2. 180-degree phase
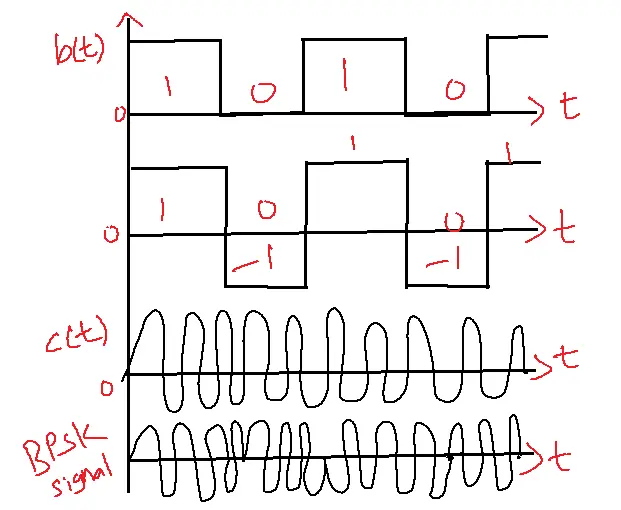
Let s1(t)=Accos(2πfct+00)—b(t)=1
S2(t)=Accos(2πfct+π)—b(t)=0
Logic 0=+1— Accos2πfct
Logic 1=-1—- Accos2πfct
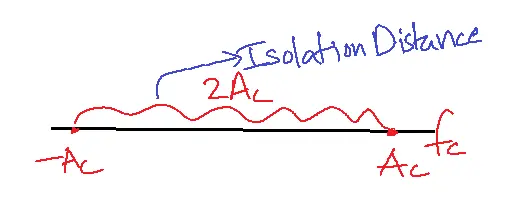
Compared to ASK, and FSK, the isolation distance for phase shift keying PSK is high.
For binary data b(t)
B(t)=r
c(t)= Accos2πfct
s1(t)= Accos2πfct b(t)=1
s2(t)=- Accos2πfct b(t)=0
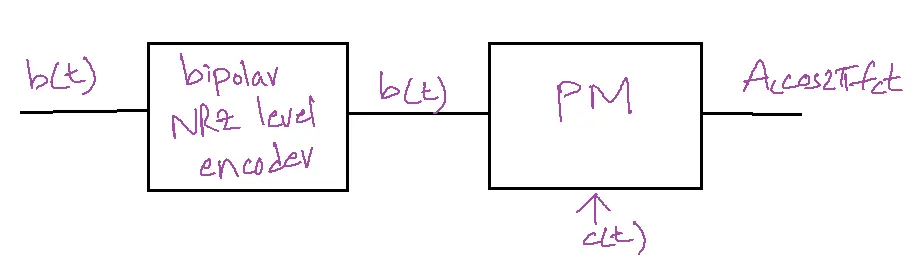
b(t)=bipolar NRZ
logic 1=+1r
logic 0= -1r
s(t)=b(t) Accos2πfct.
BPSK Modulator:
Coherent BPSK Demodulator:
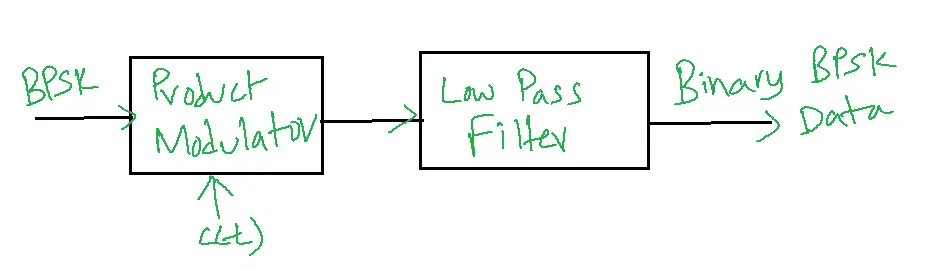
Case-1: if s(t)= Accos2πfct s(t)=s1(t)
c(t)= Accos2πfct b(t)=1
Now for PM, s1(t)= Ac2 cos 22πfct
Output is Ac2/2
Case-2: if s(t)=s2(t) b(t)=0
s2(t)= -Ac2 cos 22πfct
output is -Ac2/2
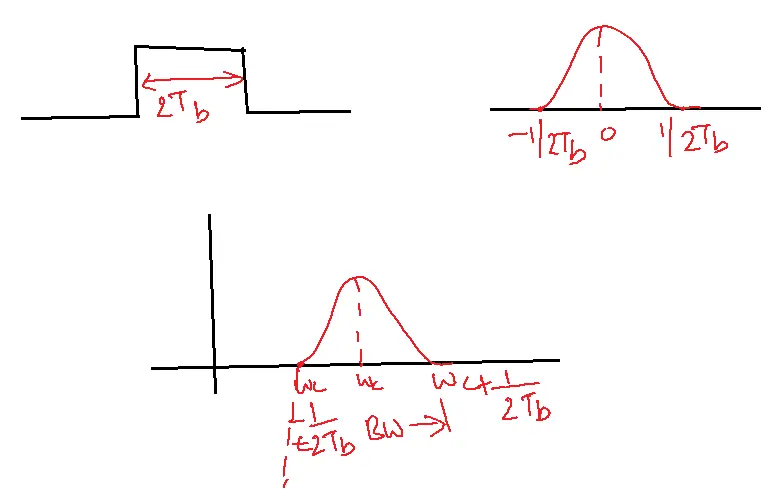
The bandwidth of phase shift keying is 2fb
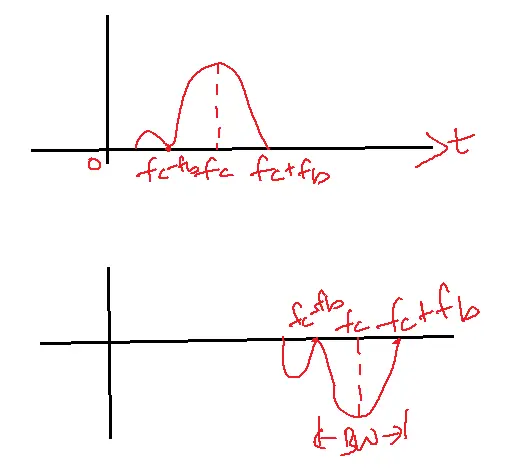
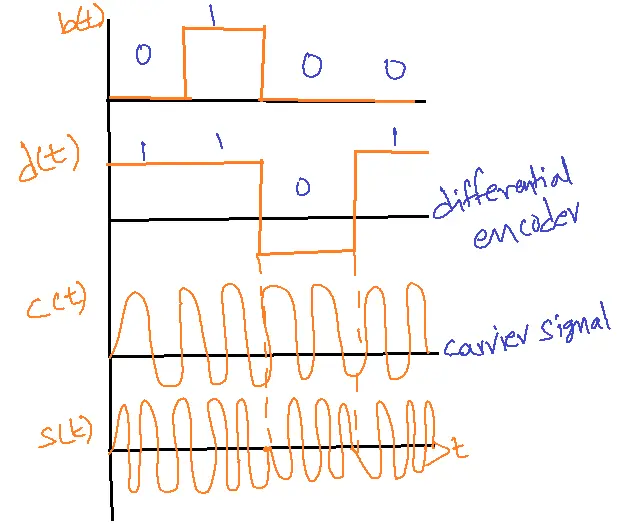
Differential Phase Shift Keying:

d(t)=b(t) exclusive OR with d(t-tb)
DPSK Demodulator:
The first-bit duration (0 to Tb)
s(t)=s1(t)
the output of PM is s(t)= – Accos2πfcts1(t)
= -Ac2 cos 24πfct
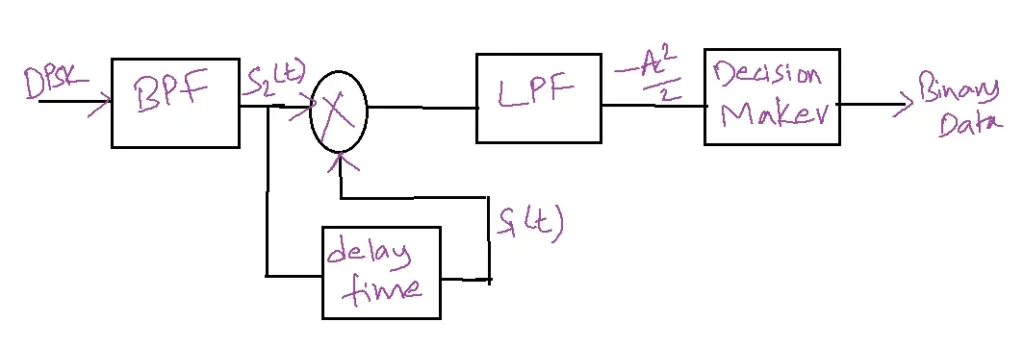
The second-bit duration (Tb to 2Tb)
The output of PM is s(t)= – Accos2πfcts1(t)s1(t)
=-Ac2/2- Ac2cos4πfct /2
For the second bit duration
Output= Ac2/2 + Ac2cos2πfct/2
QPSK Demodulator:
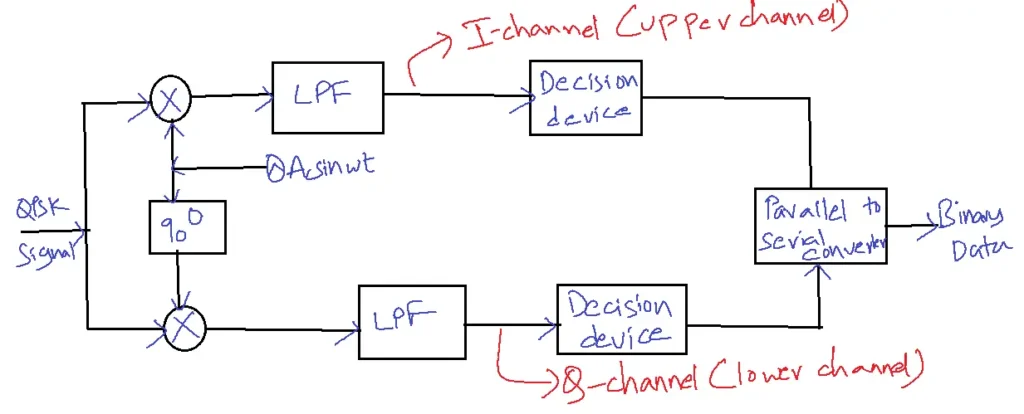
I=1,Q=0
s(t)= Acsinwct + Accoswct
I-channel:
Output of PM= Ac 2sin2 wct- Ac 2coswct+ sinwct
= Ac 2/2 – Ac 2/2 cos2wct – Ac 2/2 sin2wct
= Ac 2/2
Q-channel:
Output of phase modulation= Ac 2sinwct coswct + Ac 2coswct
= – Ac 2/2 – Ac 2/2 cos2wct + Ac 2/2 sin2wct
= – Ac 2/2
Bandwidth of QPSK:
BW=1/Tb
= Rb or fb
Example:
A voice signal sample at the rate of 8000 samples per second and each sample is encoded into 8 bits using PCM. The binary data is transmitted into free space after modulation. Determine the bandwidth of the modulated signal when the modulation is ASK, BPSK, FSK with f1=10 MHz, f2=8MHz
Solution: Rb=nfs
=8 x 8000
=64000 bits/sec
fb=64 KHz
Bandwidth of ASK = 2fb=128 KHz
Bandwidth of BPSK = 2fb= 128 KHz
Bandwidth of FSK = (f1-f2)+2fb=2 MHz+128 KHz
= 2.128 MHz
Bandwidth of QPSK=fb=64 KHz.
Advantages of PSK
1. High Spectral Efficiency: More data is transmitted within a given bandwidth.
2. Resistance to Noise and Interference: PSK signals are less susceptible to noise and interference.
3. Simple Implementation: PSK is relatively easy to implement using digital circuits.
Limitations of PSK
1. Sensitive to Phase Noise: PSK signals can be affected by phase noise in the transmitter or receiver.
2. Requires Coherent Detection: PSK signals require coherent detection, which can be complex to implement.
Applications of Phase Shift Keying:
- Wireless LANs (Wi-Fi): PSK is widely used in Wi-Fi networks to transmit data wirelessly between devices and routers. It enables high-speed internet connections for laptops, smartphones, and other devices.
- Bluetooth Communication: PSK is used in Bluetooth technology for short-range wireless communication between devices due to its efficiency and low power consumption.
- Satellite Communication: PSK is crucial for reliable data transmission between ground stations and Earth-orbiting satellites.
- Digital Television Broadcasting: PSK is utilized in digital television broadcasting standards like DVB-S and DVB-T2. It helps efficiently transmit high-quality video and audio signals to viewers’ homes.
- RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification): PSK in RFID systems identifies and tracks objects using radio waves in applications like inventory management, access control, and contactless payments.
Conclusion
Phase Shift Keying is a widely used and effective modulation technique for digital communication systems. Its advantages make it a popular choice for various applications, but its limitations should also be considered. By understanding PSK, you can better appreciate the technology behind modern communication systems.
FAQs of Phase Shift Keying:
1. What is Phase Shift Keying (PSK)?
- PSK is a digital modulation technique where the phase of a carrier wave is changed to represent digital data.
- It’s a widely used method for transmitting information over wireless and wired communication channels.
2. How does Phase Shift Keying (PSK) work?
- In PSK, the phase of the carrier signal is shifted according to the digital data being transmitted.
- Each unique phase shift corresponds to a specific symbol or bit pattern, allowing the receiver to decode the information.
3. What are the different types of PSK?
The most common types of PSK include:
- Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK): Binary 0 and 1 are represented by two phases
- Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK): QPSK leverages four phase states to achieve a higher data rate, transmitting two bits per symbol.
- 8-PSK: Eight phases are used, representing three bits per symbol.
- 16-PSK: Sixteen phases are used, representing four bits per symbol.
4. What are the advantages of PSK?
PSK offers several advantages in digital communication:
- Good noise immunity: It’s relatively resistant to noise and interference.
- Bandwidth efficiency: It offers increased data-carrying capacity within a given bandwidth compared to other modulation schemes.
- Simple implementation: It’s relatively easy to implement in hardware and software.
5. What are the applications of PSK?
PSK is used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Wireless LANs (Wi-Fi)
- Bluetooth communication
- Satellite communication
- Digital television broadcasting
- RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification)
