There are two different types of FM transmitter
1. FM Transmitter using Reactance Tube Method: ( Direct Method)
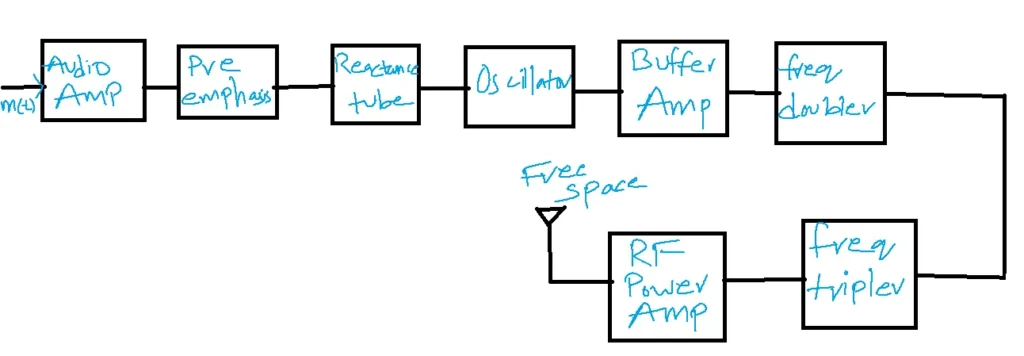
In this block diagram, the m(t) signal is given as input to the audio ample.
In an FM transmitter, the audio amplifier amplifies the message signal. The pre-emphasis circuit strengthens the signal at higher frequencies.
The combination of the reactance tube and oscillator acts as a modulator. Frequencies generated by the oscillator depend upon the voltage levels of the input message signal.
Buffer amplifiers have high input impedance so that any variations in the load cannot affect the frequency generated by the oscillator.
To increase the frequency levels, frequency multipliers such as frequency doublers, and triplers can be used in cascade. In the FM Transmitter, the RF amplifier stage amplifies the power levels of the FM signal generator and is radiated through the transmitting antenna.
2. FM Transmitter using Amstrong method [Indirect Method]:
Step-1: Generation of NBFM

The audio amplifier amplifies the m(t) and the pre-emphasis circuit strengthens m(t) at higher frequencies. The master oscillator generates the carrier frequency and the carrier amplifier amplifies the carrier. Balanced Modulator generates the DSBSC.
The combining amplifier generates an NBFM signal which is the combination of carrier, USB, and LSB [USB and LSB are out of phase with each other].
Step 2: Once NBFM is generated, it can be converted to WBFM using a cascade connection of frequency multipliers and converters [Mixers].
Frequency multipliers can be frequency doublers or triplers.
The frequency multiplier will affect both carrier frequency and delta f.
However signal combiner will affect only carrier frequency, but it will not affect frequency deviation.
The generated WBFM signal undergoes amplification in an RF power amplifier before being radiated into the frequency spectrum via a transmitting antenna.
Table of Contents
Frequency stabilization in FM Transmitters:
The frequency oscillators can be affected by the following:
i. Temperature changes
ii. Changes in supply voltage
iii. Aging of the electronic device
To improve stability the following two methods are introduced:
1. Automatic Frequency Control Method in Reactance Tube FM Transmitter:

The Limiter circuit will make the amplitude wave of FM constant.
Consider frequency generated by oscillator fc=1 MHz.
f0 crystal oscillator= 4.5 MHz. The output of the IF amplifier is 500 KHz. The discriminator is designed to give a zero DC output for this 500 KHz input.
If there is instability in fc (higher or lower) the value of delta f may be increased beyond 500K or decreased below 500K.
Depending upon the change in delta f, the discriminator generates a positive or negative DC voltage which can correct the frequency of oscillators fc.
2. Federal Telecommunication Method:

The feedback loop employs a series of frequency dividers, phase modulators, and a low-pass filter (LPF) to adjust the oscillation frequency. The frequency dividers generate an error in voltage V when there is a change in fc.
Depending upon the error voltage, the PM, and LPF generate an equivalent DC voltage, which will be given as input to the oscillator so that the frequency of oscillations will be corrected.
AUTOMATIC GAIN CONTROL (AGC CIRCUIT):

The signal strength received from the antenna will not be constant due to propagation losses also called fading.
Should the receiver’s sensitivity remain unchanged, the output signal’s intensity will still vary.
AGC (Automatic Gain Control) circuit is used to overcome this problem. AGC (Automatic Gain Control) circuit will control the overall gain of the receiver according to the variations in the receiver input signal so that the audio output is constant.
To achieve a 100W output, the receiver amplifies the input signal by a factor of 1000. The minimum signal strength required at the input is 0.1 W. If the signal strength is above the reference level, the AGC (Automatic Gain Control ) circuit will decrease the gain.
If the signal strength is below the reference level, the AGC (Automatic Gain Control) circuit will increase the gain so that the output is constant.
AGC (Automatic Gain Control) is classified into two types:
1. Simple AGC (Automatic Gain Control)
2. Delayed AGC (Automatic Gain Control)
In simple AGC (Automatic Gain Control) or in the first method the signal received from the antenna is taken as the referenced level. AGC (Automatic Gain Control) circuit will control the gain if the signal strength increases or decreases.
In the second method or Delayed AGC, action is delayed until the input signal reaches the reference level. In this case (Delayed AGC), the volume controller knob fixes the reference level.
Applications of FM Transmitter
- Car Audio Streaming: Connect your smartphone or MP3 player to your car’s stereo wirelessly, enabling you to enjoy music, podcasts, and audiobooks on the go.
- Home Audio Systems: Transmit audio from your TV, computer, or music player to wireless speakers or headphones throughout your house.
- Silent Disco: Party-goers wear wireless headphones tuned to a specific FM frequency, allowing for multiple DJs or music genres in the same space without noise complaints.
- Assistive Listening Devices (ALDs): Individuals with hearing difficulties can use FM transmitters to receive audio directly to their hearing aids or headphones, improving clarity in noisy environments.
- Drive-In Cinemas/Events: Broadcast audio directly to car radios, providing a convenient and immersive audio experience.
- Educational Settings: Teachers can use FM transmitters to ensure their voice is heard by all students, particularly those with hearing impairments.
- Public Address Systems: Transmit announcements, music, or emergency broadcasts to large audiences in stadiums, arenas, or outdoor venues.
- Tour Guide Systems: Tour guides use FM transmitters to communicate with their group while maintaining a comfortable listening experience for everyone.
- Wireless Microphones: Transmit audio from wireless microphones to speakers or recording devices, ideal for live performances, conferences, or presentations.
- Low-Power Broadcasting: FM transmitters can be used by amateurs or community radio stations to broadcast local music, news, or educational programs to a restricted geographic area.
FAQs related to the topic
Q1. What is an FM transmitter and how does it work?
- An FM transmitter is a device that sends audio signals over radio waves to FM receivers.
- It works by translating sound into electrical signals, superimposing them onto a radio wave, and transmitting these modulated waves via an antenna.
Q2. How do I choose the best FM transmitter for my car/home?
- Consider factors like transmission range, audio quality, ease of use, additional features (Bluetooth, USB charging), and compatibility with your devices (smartphone, music player).
Q3. Can I use an FM transmitter with my smartphone?
- Yes, most modern FM transmitters offer Bluetooth or auxiliary input for seamless Smartphone compatibility, allowing you to play music, podcasts, or audiobooks through your car’s stereo.
Q4. Are FM transmitters legal to use?
- In most countries, low-power FM transmitters are legal for personal use.
- However, regulations vary, so check your local laws regarding transmission power and frequency restrictions.
Q5. How do I troubleshoot common FM transmitter problems (static, interference)?
- Static and interference can often be resolved by adjusting the transmitter frequency, finding a clear channel, reducing the distance between the transmitter and receiver, or checking for loose connections.
Q6. What is the difference between an FM transmitter and a Bluetooth adapter?
- An FM transmitter broadcasts audio over radio waves, while a Bluetooth adapter creates a direct wireless connection between your device and your car stereo. FM transmitters are generally more affordable, but Bluetooth adapters often offer superior sound quality and stability.
Q7. Can I use an FM transmitter to play music from my iPod/MP3 player?
- Yes, most FM transmitters have an auxiliary (3.5mm) input, allowing you to connect older devices like iPods or MP3 players that don’t have Bluetooth functionality.
Q8. How do I improve the sound quality of my FM transmitter?
- To minimize interference, experiment with adjusting the frequency to locate a clear channel, move the transmitter and receiver closer together, utilize a high-quality audio cable, and ensure proper transmitter ground connection.
