What is Delta Modulation?
Delta Modulation (DM) is a simple and efficient analog-to-digital modulation technique used to transmit analog signals, such as audio and video, over digital communication channels.
To reduce bandwidth we used this modulation.
The basic principle of delta modulation is the difference between the original sample and the approximate sample.
Positive means logic 1.
Negative means logic 0.
In this Modulation, every sample is represented in 1 bit.
Table of Contents
How Delta Modulation Works?
1. Analog Signal: The analog signal is sampled at regular intervals.
2. Comparator: The sampled signal is compared to a reference signal.
3. Delta Encoder: The digital signal is generated by encoding the difference (delta) between the reference signal and the sampled signal
4. Digital Signal: The digital signal is transmitted over a communication channel.
5. Delta Decoder: The received digital signal is decoded to reconstruct the original analog signal.
DM transmitter:

In this modulation, PCM transmits analog signals digitally using a single-bit PCM code. In this technique, only one bit is sent per sample, indicating whether the current sample is larger or smaller in magnitude than the previous one. If the current sample is larger, a logic 1 is transmitted; if it’s smaller, a logic 0 is sent instead.
e(nTs)=x(nTs)-x^(nTs)
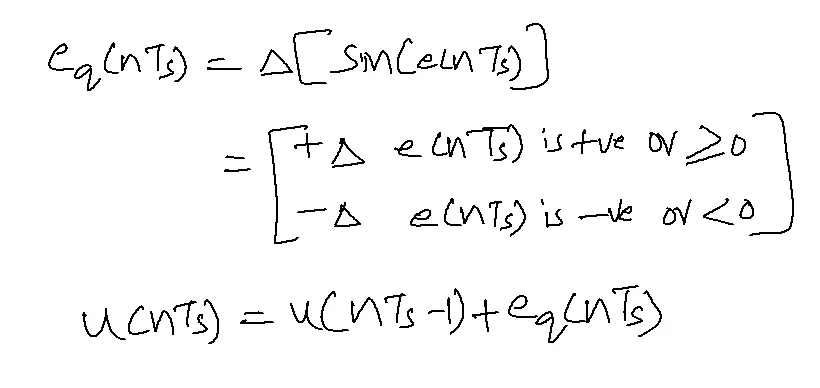
DM Receiver:
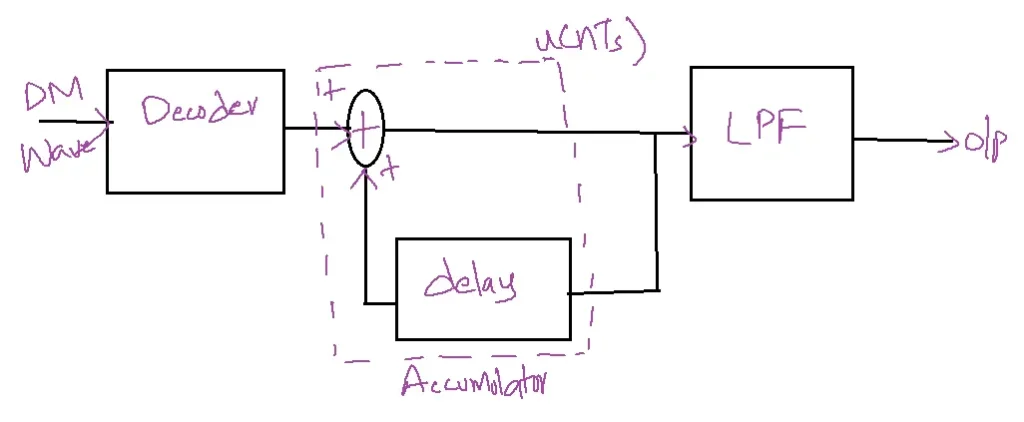
Advantages
1. Simple Implementation: DM is relatively easy to implement and understand.
2. Low Bit Rate: Digital Modulation needs a lower bit rate compared to other modulation techniques.
3. High Signal-to-Noise Ratio: DM provides a high signal-to-noise ratio, resulting in better signal quality.
4. Low Power Consumption: DM requires less power to transmit than other modulation techniques.
Disadvantages
1. Limited Dynamic Range: DM has a limited dynamic range, making it less suitable for signals with a wide range of amplitudes.
2. Slope Overload: DM can suffer from slope overload, which results in distortion and errors.
3. Granular Noise: DM can introduce granular noise, affecting signal quality.
Slope overload Distortion
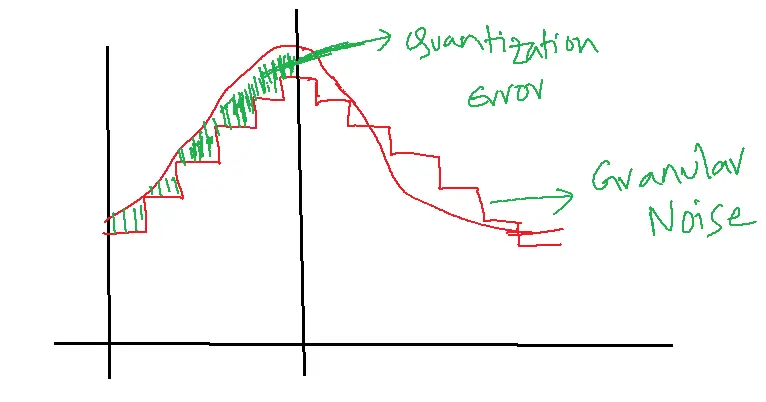
To reduce slope overload distortion, we need to increase the step size, Quantization error becomes less.
Quantization error due to the low slope of the message signal is known as Granular Noise.
Granular Noise is reduced by decreasing the Step size.
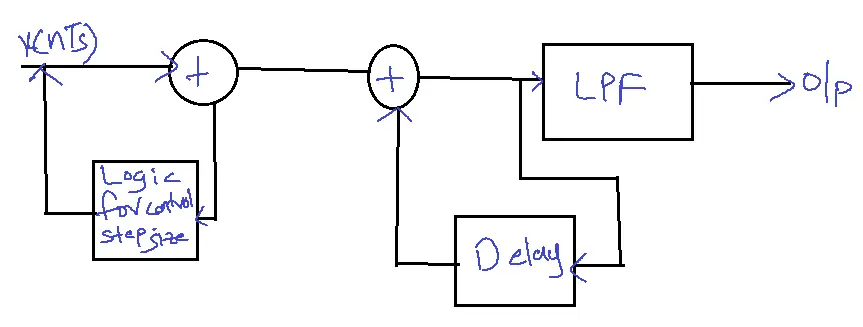
Adaptive Delta Modulation (ADM)
Adaptive Delta Modulation (ADM) is a digital modulation technique that adapts to the changing characteristics of an analog signal, optimizing its transmission over digital communication channels.
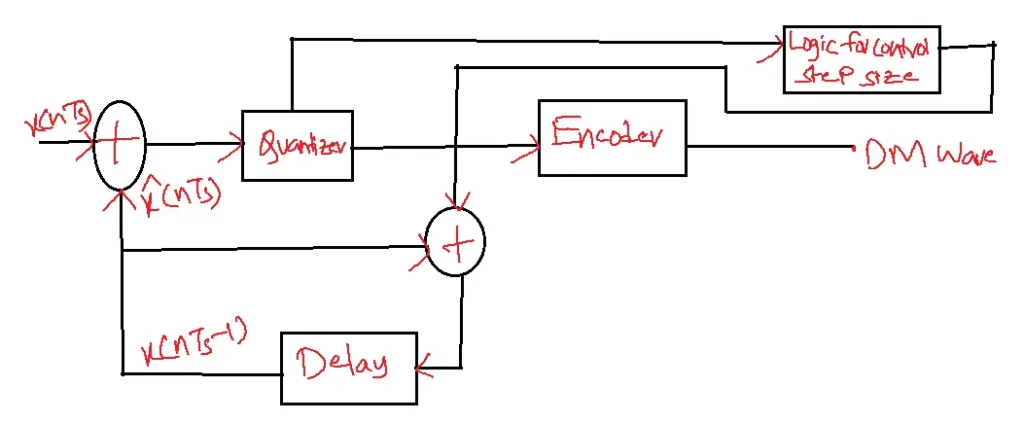
How Adaptive Delta Modulation Works?
1. Analog Signal: The analog signal is sampled at regular intervals.
2. Comparator: The sampled signal is compared to a reference signal.
3. Delta Encoder: The difference between the sampled and reference signals is converted into a digital code.
4. Adaptive Quantizer: The quantizer adapts to the changing signal characteristics, adjusting the step size and threshold levels.
5. Digital Signal: The digital signal is transmitted over a communication channel.
6. Adaptive Decoder: The received digital signal is decoded to reconstruct the original analog signal.
Advantages
1. Improved Signal Quality: ADM adapts to signal changes, reducing distortion and errors.
2. Optimized Bit Rate: ADM adjusts the bit rate according to signal complexity, reducing bandwidth requirements.
3. Robustness to Noise: ADM is more resistant to noise and interference than traditional delta modulation.
4. Low Power Consumption: ADM requires less power to transmit than other modulation techniques.
Disadvantages
1. Complex Implementation: ADM is more complex to implement traditional delta modulation.
2. Higher Computational Requirements: ADM requires more computational resources to adapt to signal changes.
3. Potential for Instability: ADM can become unstable if not properly designed or implemented.
Applications
1. Audio Compression: ADM is used in audio compression algorithms for high-quality audio transmission.
2. Image Compression: ADM is used in image compression algorithms for efficient image transmission.
3. Biomedical Signal Processing: ADM is used in biomedical signal processing for accurate signal representation.
4. Wireless Communication: ADM is used in wireless communication systems for efficient and reliable data transmission.
FAQs of Related Topic:
1. What is Delta Modulation (DM)?
- DM is a simple yet effective digital modulation technique that converts analog signals into digital ones by encoding the difference (delta) between consecutive samples.
- This allows for efficient transmission and storage of analog information in digital formats.
2. How does Delta Modulation (DM) work?
- In DM, the current input signal sample is contrasted with the previous quantized sample.
- It transmits a ‘1’ for a positive change and a ‘0’ for a negative change.
- The step size is fixed, leading to a staircase-like output waveform.
3. What are the advantages of Delta Modulation?
- Simplicity: DM has a straightforward implementation, both in hardware and software.
- Low bandwidth requirement: Its bandwidth requirements are lower than those of PCM and similar techniques.
- Robustness to noise: DM is relatively resistant to noise due to its single-bit encoding.
4. What are the disadvantages of Delta Modulation?
- Slope overload distortion: DM can suffer from slope overload distortion when the input signal changes rapidly.
- Granular noise: Quantization errors can lead to granular noise in the output signal.
5. How can the performance of Delta Modulation be improved?
- Adaptive Delta Modulation (ADM): ADM dynamically adjusts the step size based on the input signal characteristics, reducing slope overload distortion and granular noise.
